TOP - Our Business - About molding methods
FRP can be molded using the following methods
【Boats, tanks, septic tanks, housings】
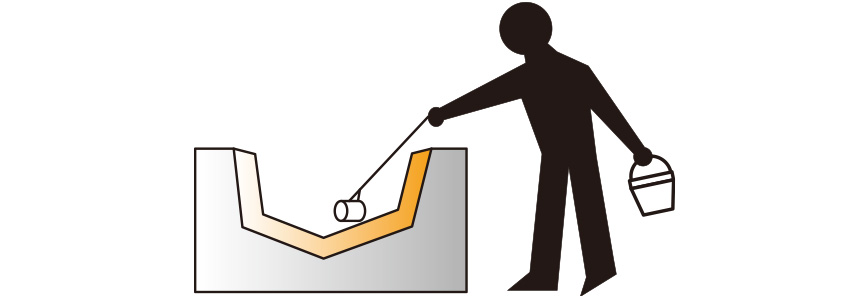
After applying a mold release agent to the mold, gel coat is applied, after curing, glass mat and cloth are set in the mold, resin is applied and impregnation curing is carried out with a roll.
【Poles, fishing rods, angles】
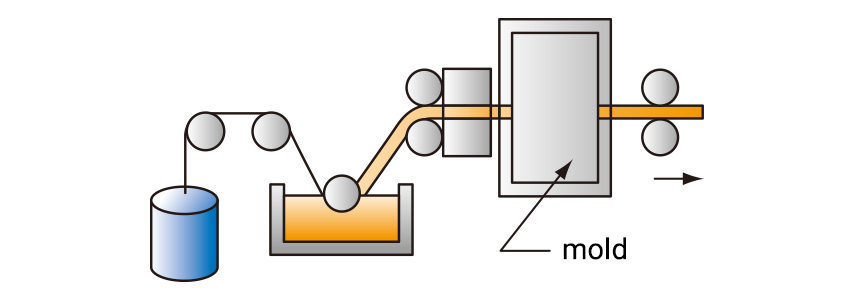
The roving is impregnated with resin in advance, heat-cured in a mold and pulled out.
【Bathtubs, septic tanks, containers, boats】
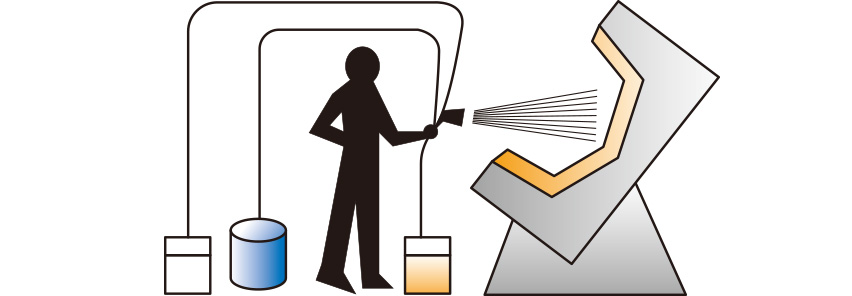
After applying a release agent to the mold, a gel coat is applied and after curing, the resin, curing agent and roving are sprayed together in a spray machine and cured.
【Pipes, tanks, ducts】
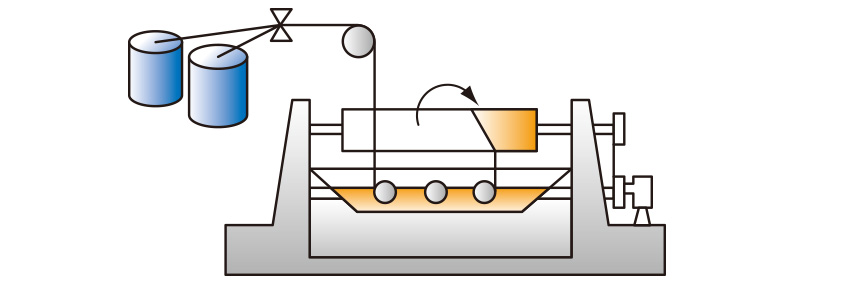
Glass roving is impregnated with resin in advance and cured by wrapping it around a rotating mandrel under tension.
【Water tanks, containers】
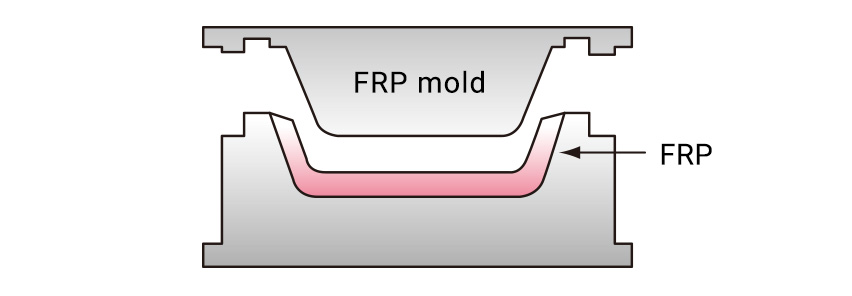
Glass mat and cloth are placed in a mold made of FRP reinforced with Resikon, resin is poured into the mold and cured by pressure impregnation.
【Pipes, tanks】
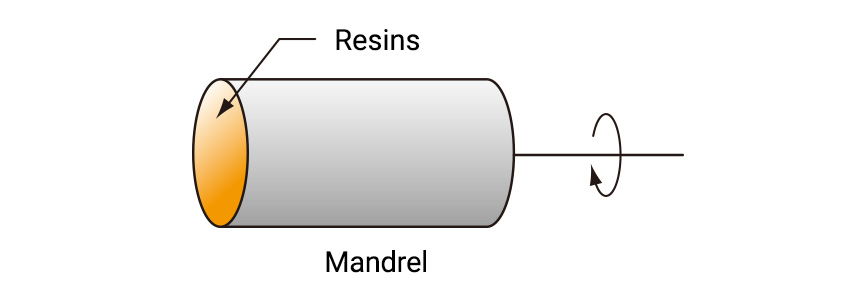
Glass mat, cloth, etc. are placed inside a hollow mandrel, and resin is poured into the mandrel while rotating, impregnating and curing.
【Bathtubs, bathroom floor pans, automotive parts】
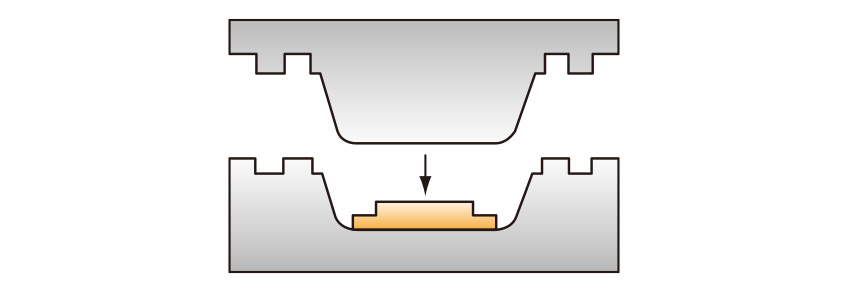
SMC cut to the required dimensions is charged into a die and cured under high temperature and pressure.
【Water tank panels, helmets】
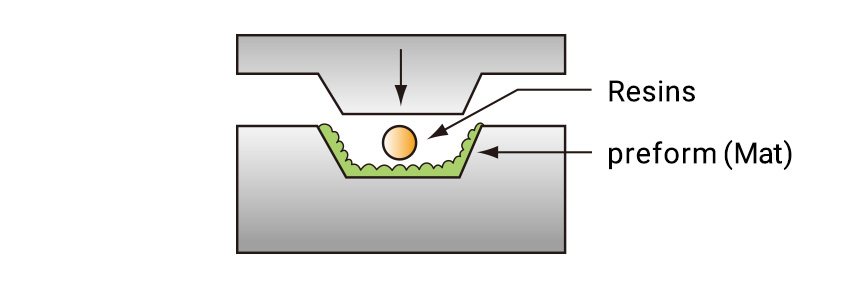
A preform prepared in advance is set in the die, charged with resin and cured at high temperature and high pressure.
POLYHOPE™ cures at both room temperature and high temperatures, and the curing time can be easily adjusted. Therefore, you can choose the molding method that best suits your purpose, from the general hand lay-up method to high-purity injection molding.
| molding method | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hand lay-up | Spray-up | Cold press | Resin injection | Preform matched die (MMD) | SMC | BMC | Filament winding | Drawing | |
| Design cost | Cheapest | Cheapest | Medium | Medium | High | High | High | Medium to high | Medium to high |
| molding material cost | Cheap | Cheap | Medium | Medium | High | High | High | Medium | Medium |
| Number of man-hours | Max | Large | Medium | Medium | Small | Small | Small | Small | Small |
| Size limit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (medium) | Yes (small) | Yes | Yes |
| Proficiency | Required | Required | Not required | Not required | Not required | Not required | Not required | Not required | Not required |
| Shape | Relatively simple | Relatively simple | Relatively simple | Relatively simple | Complex possible | Complex possible | Complex possible | Limited to rotating bodies | Limited to one direction |
| Wall thickness | Uneven | Uneven | Constant | Constant | Constant | Constant | Constant | Constant | Constant |
| Other | High labour costs | - | Gel coatings possible | Gel coatings possible | - | Joints by flow | Joints by flow | High strength | Continuous forming |
| Glass substrate | Matt glass cloth Roving cloth |
Roving cloth | Continuous matt matte | Continuous matt matte | Chopped strand | Chopped strand | Chopped strand | Roving yarn tape | Roving continuous matt |
| Normal glass content (%) | 27~45 | 30 | 25~35 | 25~35 | 30 | 25~30 | 15~25 | 50~75 | 50~70 |
| Maximum filler content (phr) | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 250 | 250 | 50 | 50 |
| Forming temperature (°C) | Room temperature | Room temperature | 15~60 | 15~60 | 100~150 | 120~150 | 120~160 | 15~60 | 130~160 |
| molding pressure (×10-1MPa) |
Contact pressure | Contact pressure | 2~5 | 1~10 | 7~21 | 7~200 | 15~140 | Winding force | Pulling force |
| molding cycle | 30min-1day | 30min-1day | 15-60min | 20-60min | 1-5min | 0.5-5min | 0.5-5min | 0.5-6m/min | 0.5-3m/min |
| Minimum thickness | 1.5mm | 1.5mm | 1.5mm | 2mm | 0.7mm | 1.3mm | 1.5mm | 2.5mm | 1.0mm |
| Maximum thickness | 25mm | 12mm | 13mm | 13mm | 7mm | 25mm | 25mm | 75mm | 50mm |
| Thickness variation | ±0.5mm | ±0.5mm | ±0.5mm | ±0.5mm | ±0.2mm | ±0.13mm | ±0.05mm | ±0.3mm | ±0.1mm |
| Minimum radius | 6.4mm | 6.4mm | 6.4mm | 6.4mm | 3.2mm | 1.4mm | 0.8mm | 3.2mm | 1.0mm |
| Material type | molded product | FRP molded products (note) | SMC molded product | Aluminium | Steel | Wood | Hard vinyl chloride |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific gravity | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.7 | 7.8 | 0.4~0.8 | 1.4 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 47 | 147 | 90 | 88 | 333~402 | 45~88 | 99~59 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 110 | 216 | 180 | 197 | - | 99~98 | 69~108 |
| Flexural modulus (GPa) | 4.4 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 68.6 | 206 | 8.0~15.0 | 2.9 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 155 | 255 | 180 | - | - | 29~59 | 59~78 |
Note: Laminates made with a glass fiber content of 30%. The physical properties listed in this table are representative values and not standard values.
Japan Composite Co., Ltd.
8th Floor, Muromachi Furukawa Mitsui Building (COREDO Muromachi 2),
2-3-1 Nihombashi-Muromachi, Chuo-ku, Tokyo 103-0022